What is In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)?
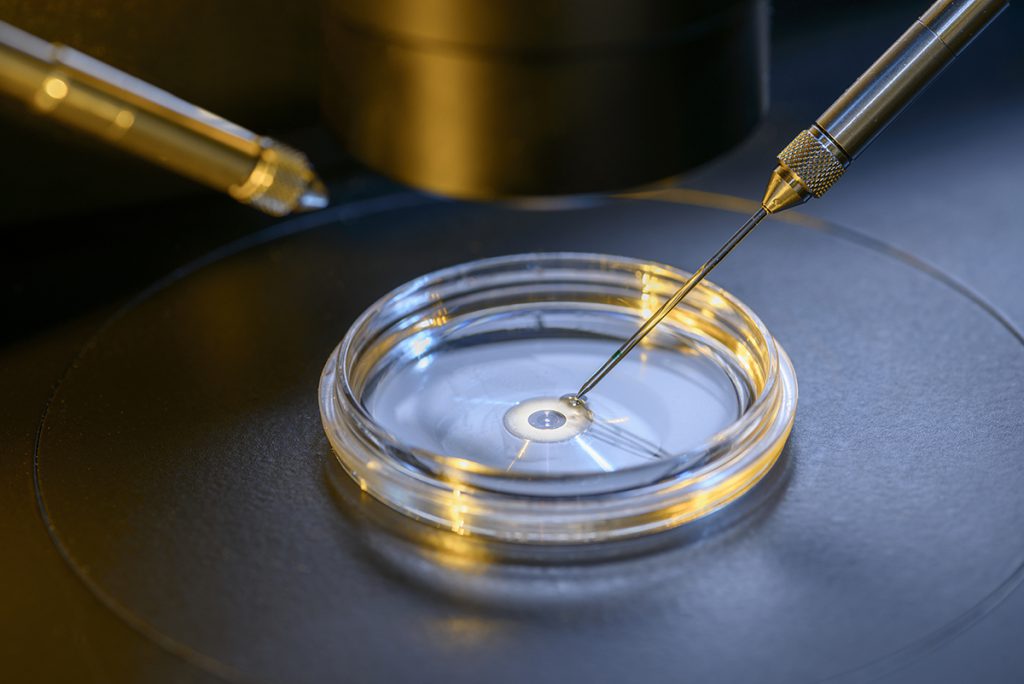
In vitro fertilization is the technique most commonly used in assisted reproduction treatments and is characterized because the union of the ovum with the sperm (fertilisation) is carried out in the laboratory, that is, outside the maternal womb. With this technique, it is always necessary to perform ovarian stimulation with drugs called gonadotrophins.
The patient herself is to administer these subcutaneously, under ultrasound and analytical control of the hormone estradiol in the blood to assess the maturation of the ovules.
The ideal is to achieve the maturation of about 8 -10 ovules in order to have good chances of success.
After a period of about twelve days of treatment, the ovules are already mature and their extraction is carried out to transfer them to the laboratory. The extraction is performed in an operating theatre, with sedation of the patient. The procedure involves puncture of the ovarian follicles performed by transvaginal ultrasound.
This process usually does not last more than 10-15 minutes. The patient then is discharged and must keep a relative rest of 24-48 hours at home.
Once in the laboratory, the obtained ovules can be inseminated with the semen of a partner or donor, or in a conventional manner, that is, placing each ovule in a culture dish together with several thousand sperm and waiting 24 hours for it to produce fertilization, or fertilize the ovum by ICSI, ICSI, a technique that involves injecting a sperm through a micropipette into the ovule with the help of a special microscope.
Currently some centers already have a new microscope that allows performing this technique at a significantly larger magnification thus being much more precise in the injection and selection of sperm. This is what is known as IMSI.
Once the ovule is fertilized with sperm, it is already an embryo that is allowed to grow in culture media and with special incubators, normally for three days undergoing a rigorous observation process regarding its morphology and number of cells. Not all embryos develop normally, some stop growing (cell block) and have to be discarded.
In some cases the embryo is allowed to grow for up to five days (Blastocyst stage), in order to be able to select its morphology in a more rigorous way and to decide which are the most suitable to implant in the uterus of the patient through an Embryo Transfer. Also to select those susceptible for freezing (Embryonic Vitrification.)
Whether in the third or fifth day, the Embryo Transfer is performed in the same manner. It involves depositing one or two embryos inside the uterus, through a special cannula (catheter). The procedure is simple and totally painless. Performed on an outpatient basis. After the procedure, it is recommended that the patient observe relative rest during 24 hours.
The same day of the transfer, any surplus of good quality embryos are frozen using the technology of Vitrification, so that they can be transferred later in a following cycle without the need of ovarian stimulation or puncture.